
Overview

International Year of Astronomy 2009
The International Year of Astronomy 2009 is a global effort initiated by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and UNESCO to help the citizens of the world rediscover their place in the Universe through the day- and night-time sky, and thereby engage a personal sense of wonder and discovery.

Communicating Astronomy with the Public Journal
Communicating Astronomy with the Public Journal (CAPjournal) is a free peer-reviewed journal for astronomy communicators, online and in print.

Europlanet
Europlanet is a network linking planetary scientists from across Europe. The aim of Europlanet is to promote collaboration and communication between partner institutions and to support missions to explore our Solar System.

Venus
Venus Express will allow studying in great detail the atmosphere of Venus, to understand its complex dynamics and its tight relationship with the surface and with the planetary space environment around it.

Navegar Foundation
The role of science communication is bringing achievements in science into the public. Popular science communication provides a bridge between the scientific community and the wider world.
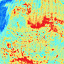
Thermal Inertia and surface properties of Mars
Thermal inertia is the key property controlling the diurnal surface temperature variations and is dependent on the physical character of the top surface.

Faraday Waves
Parametrically forced surface waves also known as faraday waves are an interesting phenomenon in fluid dynamics.
X-Red
X-red is a space mission concept designed to detect these extremely high redshifted GRBs, in order to probe the nature of the first generation of stars and hence the time of reionisation of the early Universe.
Artificial Life
Life was still not found outside Earth and therefore we still cannot make any kind of empirical generalization about the main features a chemistry must have to evolve into life or about the necessary environmental conditions.