Photodissociation branching of NH3
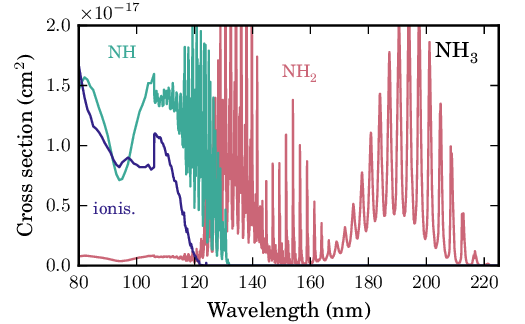
We have estimated the wavelength dependent branching ratio of NH3 into its main astrochemically-significant photodissociation products, NH2 and NH. A discussion of these cross sections is given in Heays et al. 2017, and principal sources of data are Slanger & Black 1982 and Leach et al. 2005.
[Download the NH3 partial cross sections in hdf5 format.]
We have calculated the partial photodissociation rates generating these products when exposed to various kinds of interstellar and cosmic-ray-generated radiation fields.
| NH3 ⟶ NH2 + H | NH3 ⟶ NH + 2H/H2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Radiation field1 | Rate2 | Frac.3 | Unc.4 | Rate | Frac. | Unc. |
| ISRF | 8.3e-10 | 0.58 | B | 6.1e-10 | 0.42 | B |
| Blackbody 4000K | 3.6e-09 | 1.00 | A | 2.3e-13 | 0.00 | C |
| Blackbody 10000K | 1.6e-09 | 0.95 | A | 9.0e-11 | 0.05 | B |
| Lyman-alpha | 6.6e-11 | 0.05 | B | 1.3e-09 | 0.95 | A |
| Solar | 4.0e-09 | 0.99 | A | 5.6e-11 | 0.01 | C |
| TW-Hydra | 4.9e-10 | 0.35 | A | 9.1e-10 | 0.65 | A |
| Cosmic-ray induced | 3.9e-14 | 0.39 | B | 6.2e-14 | 0.61 | B |
2 In units of s-1.
3 Estimated branching fraction between all channels producing OH and O (or NH2 and NH) regardless of excitation state or the chemical co-fragment.
4 Estimated rate uncertainties: accurate to within 30% (A), a factor of 2 (B), a factor of 10 (C).
