 |
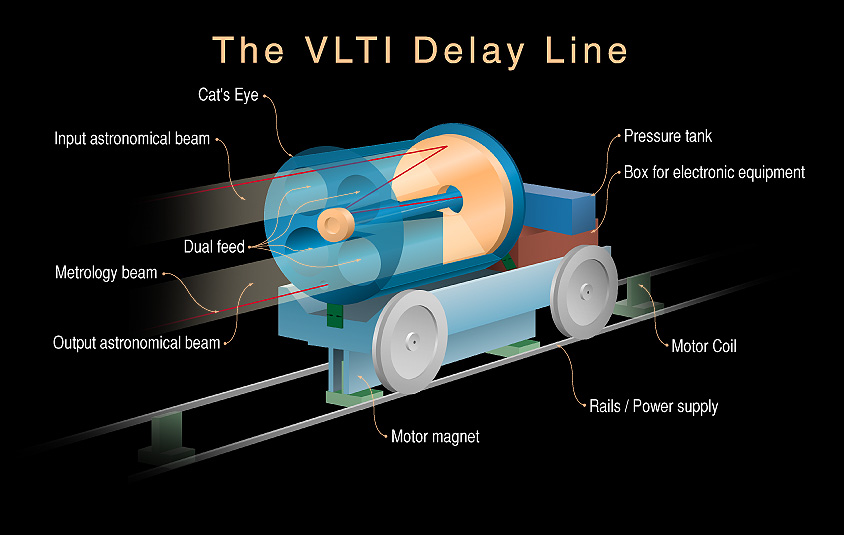
This is a schematic representation of the VLTI Delay Line, showing the retro-reflector on its moving base. It is a mechanical-optical system that will compensate the optical path differences of the light beams from the individual telescopes. Such a system is necessary to ensure that the light from all telescopes arrive in the same phase at the focal point of the interferometer in order to create sharp images. The Delay Line of the VLTI is a Fokker Space (Leiden, The Netherlands) and TNO-TPD (Delft, the Netherlands) contribution. |
| Aerial view of the Very Large Telescope being build on mount Paranal in Chile. The ESO VLT consists of an array of four 8-meter telescopes which can work independently or in combined mode. In this latter mode the VLT provides the total light collecting power of a 16 meter single telescope. The telescopes may also be used in interferometric mode providing high resolution imaging. |  |
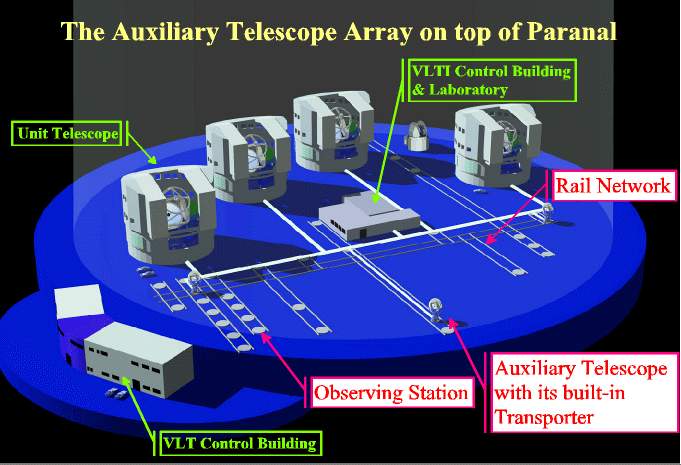 |
Schematic overview of the VLTI with its auxiliary telescopes and the associated buildings at the site. |
| One of the four unit telescopes when it was at Ansaldo in Milan. To appreciate it's size, note the car right next to it. |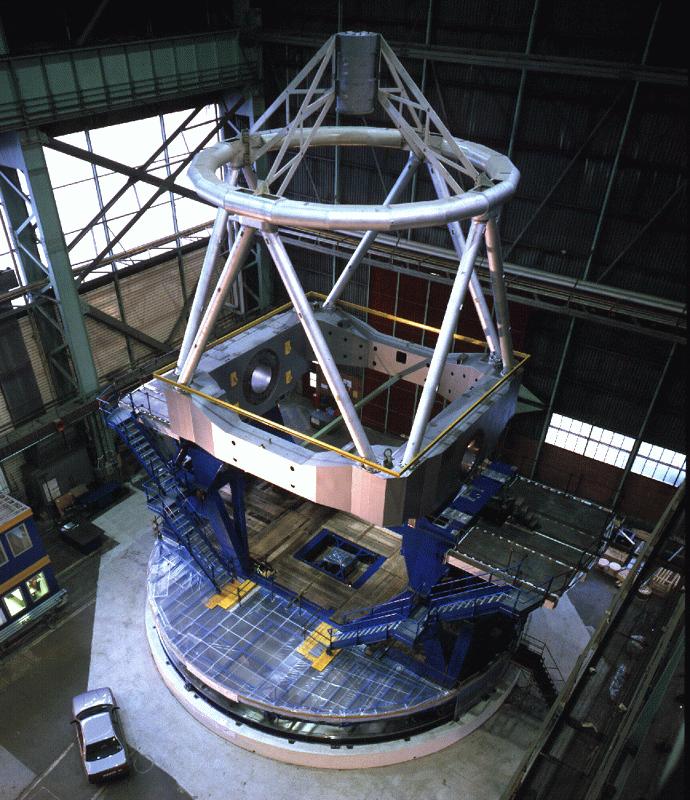  |
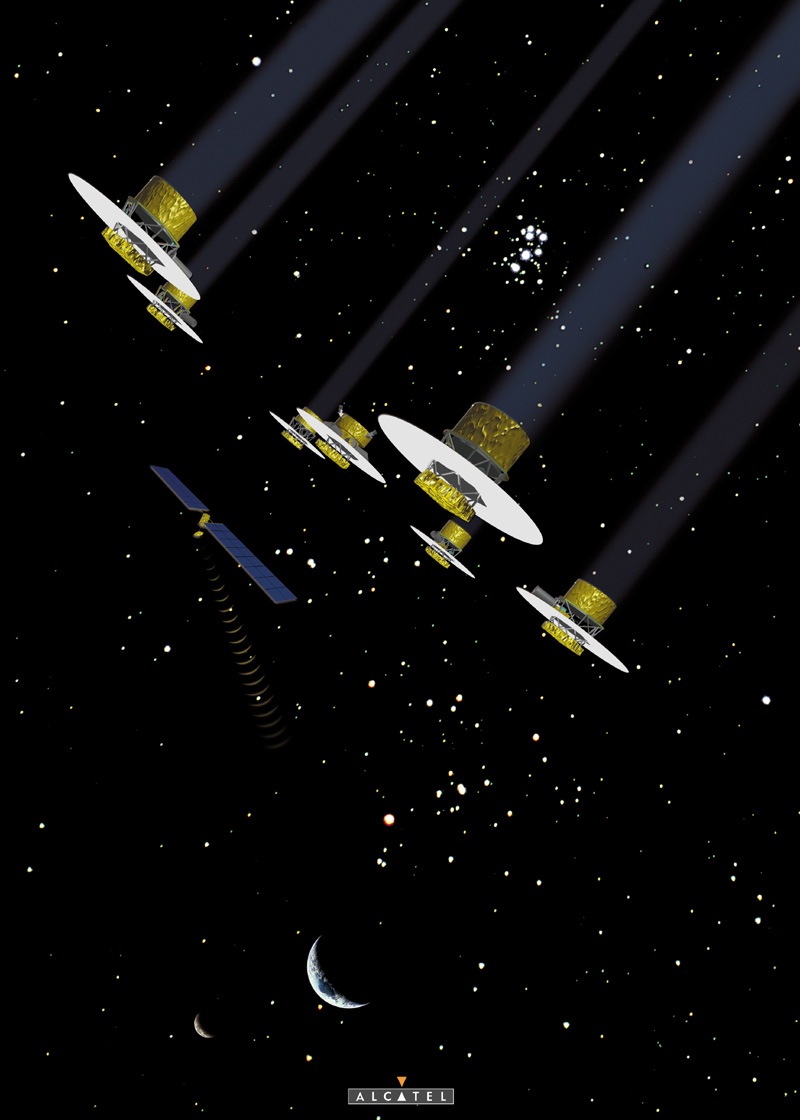 |
Artists impression of the space
project DARWIN, an infrared
interferometer. Its main goals are to
|