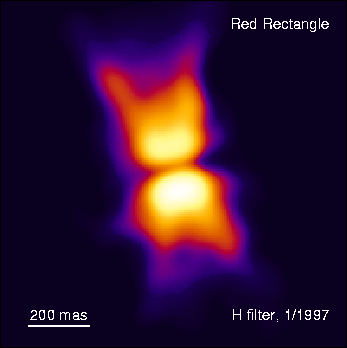|
Vincent Icke's
Web Site
|

|
Vincent Icke's
Webstek
|
eMail: icke@strw.LeidenUniv.nl
Escape Hatch
 From here, you can go back to the Home Page of Sterrewacht Leiden
From here, you can go back to the Home Page of Sterrewacht Leiden
or to the Home Page of the Sterrewacht
Theory Group
or to my own
home page
Recent observations of the Red
Rectangle, made with the Hubble
Space
Telescope, show exquisite detail of the outflow from the central
double
star. I predicted this double-cone pattern in the 1981 Astrophysical Journal. The development of extremely fast
computers has enabled me to revisit this work. The computed flow
patterns match the observations in great detail. I have written a popular account for all to read,
and to enjoy! The attached page of links
to Scientific Details goes into the subject
more deeply.
Planetary Nebula Hydrodynamics:
Movies of Numerical Work
See the printed papers on my PN site, or browse in the electronic
issues of Astronomy
&Astrophysics. Caution Websurfers:
these movies take quite a while to download! They are
given in two formats: one low-quality at high compression, and
one high quality that has about twice the size of the compressed
version. For people with slower line connections, I have included
a few movies of low-resolution simulations. All movies are
in QuickTime format (Movie JPEG A-compression).
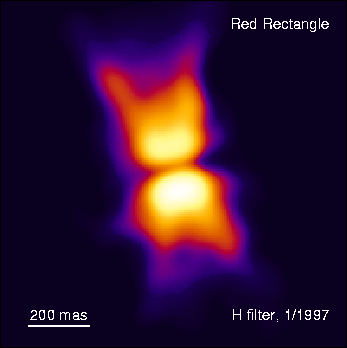 The
Red Rectangle: Observations in H-band by Menschchikov et al.
The
Red Rectangle: Observations in H-band by Menschchikov et al.
 I have a long-standing interest in
this peculiar object; see
Are Bipolar Nebulae Biconical?, 1981 Astrophys.J. 247, 152
I have a long-standing interest in
this peculiar object; see
Are Bipolar Nebulae Biconical?, 1981 Astrophys.J. 247, 152
Currently, I am working on extracting realistic
appearances from the hydro simulations shown below. This includes
computing the appearance in reflected light, and the ionization
structure (to apply to cases like this with hot central stars).

The Red Rectangle: Conical Outflow
In these computations, the fast-wind flow from the central
star is supposed to be strongly focused by the reverse shock around
the white dwarf. This causes `shock refraction', so that the flow
leaves the central region in essentially a biconical shape. The
inner regions cannot be resolved simultaneously with the outer
flow without extreme computational expense. Therefore, the biconical
flow is taken as given. The flow is pulsed, because Van Winckel's
observations clearly indicate the presence of a train of shocks
propagating outward. The computations were done with my FCT/LCD
hydrocode on an Apple Macintosh G4.
Biconical Nebula Shaped by a
Biconical Supersonic
Outflow: B
 Click to
enlarge
Click to
enlarge
|
Numerical
computation of a pulsed biconical gas stream shooting into a
homogeneous atmosphere. Grid size 120x240 cells, quadrupled. The flow
is adiabatic with Poisson index 5/3 (monatomic gas). In this composite
image, red indicates the density, green the temperature, and blue the
velocity of the gas. The image is cylindrically symmetric about the
horizontal axis. The dying star, which is now a young white dwarf, is
in the centre of the image. You can download a medium quality movie (1.0
Mb) in QuickTime format. |
Biconical Nebula Shaped by a
Biconical Supersonic
Outflow: B
 Click to
enlarge
Click to
enlarge
|
Outflow model B (see
above). In this composite image, red indicates the density, green the
gas pressure, and blue the velocity of the gas. The image is
cylindrically symmetric about the horizontal axis. The dying star,
which is now a young white dwarf, is in the centre of the image. You
can download a medium
quality movie (1.2 Mb) in QuickTime format. |
Biconical Nebula Shaped by a
Biconical Supersonic
Outflow: A
 Click to
enlarge
Click to
enlarge
|
Numerical
computation of a biconical gas stream shooting into a homogeneous
atmosphere. Grid size 250x500 cells, quadrupled. The flow is adiabatic
with Poisson index 1.1 (to simulate the effects of cooling by assuming
high compressibility). In this composite image, red indicates the
density, green the temperature, and blue the velocity of the gas. The
image is cylindrically symmetric about the horizontal axis. The dying
star, which is now a young white dwarf, is in the centre of the image.
You can download a medium
quality movie (3.3 Mb) in
QuickTime format. |
Biconical Nebula Shaped by a
Biconical Supersonic
Outflow: A
 Click to
enlarge
Click to
enlarge
|
Outflow model A (see
above). In this composite image, red indicates the density, green the
gas pressure, and blue the velocity of the gas. The image is
cylindrically symmetric about the horizontal axis. The dying star,
which is now a young white dwarf, is in the centre of the image. You
can download a medium
quality movie (3.4 Mb) in QuickTime format. |
Biconical Nebula Model A: Gas
Density
 Click to
enlarge
Click to
enlarge
|
Outflow model A (see
above). This image shows the gas density: red indicates high values,
and blue low. The image is cylindrically symmetric about the horizontal
axis. The dying star, which is now a young white dwarf, is in the
centre of the image. You can download a high quality movie (8.4
Mb) in QuickTime format. |
Biconical Nebula Model A:
Pressure
 Click to
enlarge
Click to
enlarge
|
Outflow model A (see
above). This image shows the gas pressure: red indicates high values,
and blue low. The image is cylindrically symmetric about the horizontal
axis. The dying star, which is now a young white dwarf, is in the
centre of the image. You can download a high quality movie (9 Mb)
in QuickTime format. |
Biconical Nebula Model A:
Temperature
 Click to
enlarge
Click to
enlarge
|
Outflow model A (see
above). This image shows the gas temperature: red indicates high
values, and blue low. The image is cylindrically symmetric about the
horizontal axis. The dying star, which is now a young white dwarf, is
in the centre of the image. You can download a high quality movie (9 Mb)
in QuickTime format. |
Biconical Nebula Model A:
Velocity
 Click to
enlarge
Click to
enlarge
|
Outflow model A (see
above). This image shows the gas velocity: red indicates high values,
and blue low. The image is cylindrically symmetric about the horizontal
axis. The dying star, which is now a young white dwarf, is in the
centre of the image. You can download a high quality movie (8.1
Mb) in QuickTime format. |
Deze webstek verandert op veranderlijke wijze
Laatst gewijzigd op 14-05-04
Sleutelwoorden: Astrofysica - Kosmologie -
Hydrodynamica - Beeldende kunst
This Page Changes in Unpredictable Ways
Last Modified 14-05-04
Keywords: Astrophysics - Cosmology -
Hydrodynamics - Visual Art