|
Vincent Icke's
Web Site
|
 |
Vincent Icke's
Webstek
|
eMail: icke@strw.LeidenUniv.nl
Escape Hatch
 From here, you can go back to the Home Page of Sterrewacht Leiden
or to the Home Page of the Sterrewacht
Theory Group
From here, you can go back to the Home Page of Sterrewacht Leiden
or to the Home Page of the Sterrewacht
Theory Group
Planetary Nebula Hydrodynamics:
Movies of Numerical Work
See the printed papers on my PN site, or browse in the electronic
issues of Astronomy
&Astrophysics. Caution Websurfers:
these movies take quite a while to download! They are
given in two formats: one low-quality at high compression, and
one high quality that has about twice the size of the compressed
version. For people with slower line connections, I have included
a few movies of low-resolution simulations. All movies are
in QuickTime format (Movie JPEG A-compression).
Case 1: Conical Inflow
In these computations, the inflow from the central star is
initially in the form of a hollow cone, due to the (unseen) focusing
of the inner shock around the white dwarf. The shape of the outer
nebula is not very strongly influenced by this choice, as we will
see below in the simulations that start from a spherical inflow.
Bipolar Nebula Shaped by a Conical Supersonic
Inflow
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
|
Numerical computation
of a conical gas stream shooting into a slightly flattened atmosphere.
In this composite image, red indicates the density, green the
temperature, and blue the velocity of the gas. The image is cylindrically
symmetric about the horizontal axis. The dying star, which is
now a young white dwarf, is in the centre of the image. The image
of Mz3 roughly corresponds to the red part. You can download
a low-quality movie
(2.9 Mb) or a high quality
movie (4.4 Mb). Both movies are in QuickTime format. |
The image of Mz3 as seen in the sky is not the same as what
you see in this simulation. The reason is, that the nebula is
illuminated by the strong light source in the centre. This probably
causes the "legs" and other wisps surrounding the "ant's body".
Part of the emission of the nebula is obscured somewhat by an
equatorial belt crossing the star, seen edge-on. This is all that
remains of the "solar system" that probably orbited
around the central star of Mz3. Note the prominent bubble caps
sticking out of the main lobes of this bipolar nebula. My simulations
show that this remarkable feature is due to an inward deflection
of the highly supersonic gas that bounces off the inner walls
of the nebula, causing a double vortex that moves outward with
great violence. You can see this happen as you play the movie.
Conical Supersonic Inflow: density, temperature,
velocity
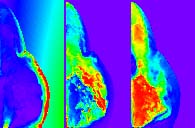 |
Numerical computation
of a conical gas stream shooting into a slightly flattened atmosphere.
In this movie, the leftmost panel indicates the density, the
middle panel shows the temperature, and the rightmost one the
velocity of the gas. The dying star is in the bottom-left corner
of each image. The colour red indicates high values, blue is
low. The image is cylindrically symmetric about the vertical
axis, and reflection-symmetric about the bottom line. You can
download a low-quality
movie (1.9 Mb) or a high
quality movie (4.5 Mb). Both movies are in QuickTime format. |
Notice also the parabolic caps sticking out at the ends, and
the rings around the waistline and around the main bubbles. These
are due to turbulent ripples propagating up into the cavities
blown by the wind from the central star. This effect is clearly
visible in these movies where you see the flow in cross section.
Conical Supersonic Inflow: density
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
|
Numerical computation
of a conical gas stream shooting into a slightly flattened atmosphere.
In this movie you see only the density of the gas. Red indicates
high values, blue is low. The image is cylindrically symmetric
about the horizontal axis. You can download a low-quality
movie (3.7 Mb) or a high
quality movie (5.2 Mb). Both movies are in QuickTime format. |
Conical Supersonic Inflow: temperature
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
|
Numerical computation
of a conical gas stream shooting into a slightly flattened atmosphere.
In this movie you see only the temperature of the gas. Red indicates
high values, blue is low. The image is cylindrically symmetric
about the horizontal axis. You can download a low-quality
movie (4.4 Mb) or a high
quality movie (6.5 Mb). Both movies are in QuickTime format.
This type of temperature distribution ought to be observable
in X-rays. |
Conical Supersonic Inflow: velocity
 Click to enlarge
Click to enlarge
|
Numerical computation
of a conical gas stream shooting into a slightly flattened atmosphere.
In this movie you see only the velocity of the gas. Red indicates
high values, blue/purple is low. Notice that the velocity drops
abruptly beyond the red region: this is a shock wave.
The image is cylindrically symmetric about the horizontal axis.
You can download a low-quality
movie (3.8 Mb) or a high
quality movie (5.3 Mb). Both movies are in QuickTime format. |
Deze webstek verandert op veranderlijke wijze
Laatst gewijzigd op 15-01-01
Sleutelwoorden: Astrofysica - Kosmologie
- Hydrodynamica - Beeldende kunst
This Page Changes in Unpredictable Ways
Last Modified 15-01-01
Keywords: Astrophysics - Cosmology
- Hydrodynamics - Visual Art







